A New System of Rule
In the face of invasions by Vikings, Muslims, and Magyars, kings and emperors were too weak to maintain law and order. People needed to defend their homes and lands. In response to that basic need for protection, a new system, called feudalism, evolved.
Feudalism was a loosely organized system of rule in which powerful local lords divided their large landholdings among the lesser lords. In exchange for land, these lesser lords, or vassals, pledged service and loyalty to the greater lord.
The relationship between lords and vassals was established by custom and tradition. A lord granted his vassal a fief (FEEF), or estate. Estates ranged from a few acres to hundreds of square miles and included peasants to work the land, as well as any towns or buildings on the land. Besides granting the estate, the lord also promised to protect his vassal.
In return, the vassal pledged loyalty to his lord. He also agreed to provide the lord with 40 days of military service each year, certain money payments, and advice.
Lords, Vassals, and Knights
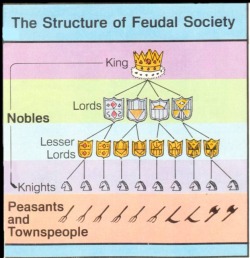
Everyone had a place in feudal society, as the chart at left shows. Below the monarch were the most powerful lords—dukes and counts— who held the largest fiefs. Each of these lords had vassals, and these vassals in turn had their own vassals. In many cases, the same man was both vassal and lord—vassal to a more powerful lord above him and lord to a less powerful vassal below him.
Because vassals often held fiefs from more than one lord, feudal relationships grew very complex. A vassal who had pledged loyalty to several lords could have serious problems if his overlords quarreled with each other. What was he to do if both demanded his aid? To solve this problem, a vassal usually had a liege lord to whom he owed his first loyalty.
In the face of invasions by Vikings, Muslims, and Magyars, kings and emperors were too weak to maintain law and order. People needed to defend their homes and lands. In response to that basic need for protection, a new system, called feudalism, evolved.
Feudalism was a loosely organized system of rule in which powerful local lords divided their large landholdings among the lesser lords. In exchange for land, these lesser lords, or vassals, pledged service and loyalty to the greater lord.
The relationship between lords and vassals was established by custom and tradition. A lord granted his vassal a fief (FEEF), or estate. Estates ranged from a few acres to hundreds of square miles and included peasants to work the land, as well as any towns or buildings on the land. Besides granting the estate, the lord also promised to protect his vassal.
In return, the vassal pledged loyalty to his lord. He also agreed to provide the lord with 40 days of military service each year, certain money payments, and advice.
Lords, Vassals, and Knights
Everyone had a place in feudal society, as the chart at left shows. Below the monarch were the most powerful lords—dukes and counts— who held the largest fiefs. Each of these lords had vassals, and these vassals in turn had their own vassals. In many cases, the same man was both vassal and lord—vassal to a more powerful lord above him and lord to a less powerful vassal below him.
Because vassals often held fiefs from more than one lord, feudal relationships grew very complex. A vassal who had pledged loyalty to several lords could have serious problems if his overlords quarreled with each other. What was he to do if both demanded his aid? To solve this problem, a vassal usually had a liege lord to whom he owed his first loyalty.
For more informations please click on one of the links below
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feudalism
http://library.thinkquest.org/10949/fief/hifeudal.html
http://library.thinkquest.org/10949/fief/hifeudal.html
